The cause and medicine for acne
The cause and medicine for acne
Bright Zoom Doctor,
Definition :
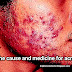
Acne is a chronic, inflammatory skin condition that occurs on the face, shoulders, back, neck, chest and upper arms.
Home remedies
There are many recommended home remedies for acne, but not all of them are supported by research.
Food
It is not clear what role diet plays in the worsening of acne. Scientists have found that people who eat a good supply of vitamins A and E and zinc have a lower risk of developing severe acne. One review describes the link between acne and diet as "controversial", but says a diet with a low glycemic load may help.
Tea oil
The results of a study of 60 patients published in the Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology show that 5 per cent tea tree oil can help treat mild to moderate acne.
If you want to buy tea tree oil, there is a great selection online with thousands of customer reviews.
Tea
There is some evidence that polyphenols from tea, including green tea, can be used in topical preparations to reduce skin production and benefit from the treatment of acne. However, the compounds in this case were extracted from the tea rather than used directly in the tea.
Moisturizers
These heal the skin, especially in people who use acne treatment such as isotretinoin, the researchers say. Moisturizers containing at least 10 percent or witch brown cactus have a soothing and potent anti-inflammatory effect.
Reasons
Human skin has pores that connect the oil glands under the skin. The follicles attach the glands to the pores. The follicle is the tiny sac that makes and secretes fluid.
The glands produce an oily fluid called skin. The skin carries dead skin cells through the follicles to the surface of the skin. A small hair grows from the skin through the follicle.
When these pores are blocked, pimples will grow and oil will grow under the skin.
Skin cells, skin and hair can stick together in one plug. This plug is infected with bacteria and causes inflammation. A pimple begins to form when the plug begins to break.
Propionibacterium agnus (P. agnes) is the name of a bacterium that lives in the skin and contributes to the infection of pimples.
Research shows that the severity and frequency of acne depends on the type of bacterial infection. Not all acne bacteria cause pimples. A strain helps to keep the skin without pimples.
Hormonal factors
Various factors trigger acne, but the main reason is thought to be an increase in androgen levels.
Androgen is a type of hormone whose levels rise during adolescence. In women, it is converted to estrogen.
As the androgen levels increase, so do the sebaceous glands under the skin. The enlarged gland produces more skin. Excess skin breaks down the cellular walls in the pores, causing bacteria to grow.
Other possible triggers
Some studies suggest that genetic factors may increase the risk.
Other reasons include:
Some drugs that contain androgen and lithium
Grease makeup
Hormonal changes
Emotional stress
Menstruation
Types
Acne pimples vary in size, color and amount of pain.
The following types are possible:
Whiteheads: These are under the skin and are small
Blackheads: Clearly visible, they are black and appear on the surface of the skin
Papules: Small, usually pink bumps, these are visible on the surface of the skin
Pustules: Clearly visible on the surface of the skin. They are red at their base and have pus at the top
Nobules: Clearly visible on the surface of the skin. They are large, solid, painful pimples that are embedded deep in the skin
Cysts: Clearly visible on the surface of the skin. They are painful and filled with pus. Cysts can cause scars.
Treatment
Treatment depends on how severe and persistent the acne is.
Mild acne
Mild acne can be treated with over-the-counter (OTC) medications, such as gels, soaps, pads, creams, and lotions, that are applied to the skin.
Creams and lotions are best for sensitive skin. Alcohol-based gels dry the skin and are better for oily skin.
OTC acne remedies may contain the following active ingredients:
Resorcinol: helps break down blackheads and whiteheads
Benzoyl peroxide: kills bacteria, accelerates the replacement of skin, and slows the production of sebum
Salicylic acid: assists the breakdown of blackheads and whiteheads and helps reduce inflammation and swelling
Sulfur: exactly how this works is unknown
Retin-A: helps unblock pores through cell turnover
Azelaic acid: strengthens cells that line the follicles, stops sebum eruptions, and reduces bacterial growth. There is cream for acne, but other forms are used for rosacea.
It is advisable to start with the lowest strengths, as some preparations can cause skin irritation, redness, or burning on first use.
These side effects normally subside after continued use. If not, see a doctor.
Treating moderate to severe acne
A dermatologist or dermatologist can treat the most severe cases.
They may prescribe a gel or cream similar to OTC medications but stronger or oral or topical antibiotic.
Corticosteroid injection
If an acne cyst is severely inflamed, it can break down. This can lead to scarring.
A swollen cyst can be treated by a specialist with dilute corticosteroid injection.
This will help prevent scarring, reduce inflammation, and speed healing. The cyst will rupture in a few days.
Oral antibiotics
Oral antibiotics may be prescribed for up to 6 months in patients with moderate to severe acne.
These are aimed at reducing the population of P. acnes. When the acne clears up the size starts to increase and decrease.
P. Acne can become antibiotic resistant in a timely manner, requiring another antibiotic. Acne is more resistant to topical than oral antibiotics.
Antibiotics fight the growth of bacteria and reduce inflammation.
Erythromycin and tetracycline are commonly prescribed for acne.
Oral contraception
Oral contraceptives can help women control acne by suppressing excess gland. They are commonly used as a long-term acne treatment.
These do not apply to women:
There is a clotting disorder
Smoke
Has a history of migraines
Over 35s
It is important to check with a gynecologist first.
Topical antibiotics
Topical antibiotics are also aimed at reducing B acne in patients with moderate to severe acne. Examples are clindamycin and sodium sulfacetamide.
The dermatologist may prescribe a topical retinoid.
Topical retinoids contain vitamin A. Is a descendant of.
Examples of topical retinoids recommended in the United States are adapalene, dazarodine, and tretinoin.
Isotretinoin
It is a strong, oral retinoid that is used to treat severe cystic acne and acute acne, which does not respond to other medications and treatments.
It is a strictly controlled drug with severe side effects. The consent form must be signed to say that the patient understands the risks.
Adverse effects include dry skin, dry lips, nose bleeds, abnormalities of the fetus and mood swings if used during pregnancy.
Patients taking isotretinoin should avoid vitamin A supplements as these can lead to vitamin A toxicity.
The cause and medicine for acne
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:










No comments