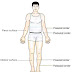
ENDOCRINOLOGY-Acromegaly: symptoms
Acromegaly: symptoms
ABCDEF:
- Arthralgia/ Arthritis
- Blood pressure raised
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Diabetes
- Enlargemed organs
- Field defect

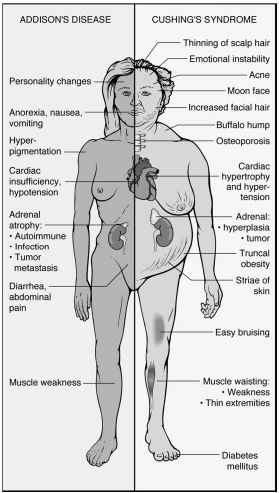
Addison's disease: features
ADDISON:
- Autoimmune
- DIC (meningcoccus)
- Destruction by cancer, infection, vascular insufficiency
- Iatrogenic
- Sarcoidosis, granulomatous such as TB histiomycosis
- hypOtension/ hypOnatermia
- Nelson's syndrome [post adrelectomy, increased ACTH]
Adrenal disorders: Cushing's vs Addison's
- Cushing: is Gushing cortisol.
- In Addison's: patient's cortisol doesn't Add up.
Adrenal gland: functions
ACTH:
- Adrenergic functions
- Catabolism of proteins/ Carbohydrate metabolism
- T cell immunomodulation
- Hyper/ Hypotension (blood pressure control)
Adrenal cortex: layers and products
"Get your Facts Right, Men are Glued to their Gonads":
- Glomerulosa
- Fasciculata
- Reticularis
- Mineralocorticoids
- Glucocorticoids
- Gonadocorticoids [androgens]
Carcinomas having tendency to metastasize to bone
"Particular Tumours Love Killing Bone":
- Prostate
- Thyroid
- Lung
- Kidney
- Breast
Corticosteroids: adverse side effects
CUSHINGS BAD MD:
- Cataracts
- Up all night (sleep disturbances)
- Suppression of HPA axis
- Hypertension/ buffalo Hump
- Infections
- Necrosis (avascular)
- Gain weight
- Striae
- Bone loss (osteoporosis)
- Acne
- Diabetes
- Myopathy, moon faces
- Depression and emotional changes
Cushing syndrome
CUSHING:
- Central obesity/ Cervical fat pads/ Collagen fiber weakness/ Comedones (acne)
- Urinary free corisol and glucose increase
- Striae/ Suppressed immunity
- Hypercortisolism/ Hypertension/ Hyperglycemia/ Hirsutism
- Iatrogenic (Increased administration of corticosteroids)
- Noniatrogenic (Neoplasms)
- Glucose intolerance/ Growth retardation

Diabetic ketoacidosis: I vs. II
- ketONE bodies are seen in type ONE diabetes.

Diabetic ketoacidosis: management
FUCKING:
- Fluids (crytalloids)
- Urea (check it)
- Creatinine (check it)/ Catheterize
- K+ (potassium)
- Insulin (5u/hour. Note: sliding scale no longer recommended in the UK)
- Nasogastic tube (if patient comatose)
- Glucose (once serum levels drop to 12)
Goitre: differential
GOITRE:
- Goitrogens
- Onset of puberty
- Iodine deficiency
- Thyrotoxicosis/ Tumor/ Thyroiditis [Hashimoto's]
- Reproduction [pregnancy]
- Enzyme deficiencies
Gynecomastia: causes
DaLAS:
- Digitalis
- Leydig cell tumors
- Alcohol
- Sertoli cell tumors
Gynaecomastia: causing drugs
DISCOS:
- Digoxin
- Isoniazid
- Spironolactone
- Cimetidine
- Oestrogens
- Stilboestrol
Gynecomastia: common causes
GYNECOMASTIA:
- Genetic Gender disorder (Klinefelter)
- Young boy (pubertal)*
- Neonate*
- Estrogen
- Cirrhosis/ Cimetidine/ Ca Channel blockers
- Old age*
- Marijuana
- Alcoholism
- Spironolactone
- Tumors (Testicular & adrenal)
- Isoniazid/ Inhibition of testosterone
- Antineoplastics (Alkylating Agents)/ Antifungal(ketoconazole)
*Asterisk indicates physiologic cause.
Hirsutism vs. virilism
- Hirsutism: Hair on body like a male.
- Virilism: Voice and rest of secondary sexual characteristics like a male.
 Hirsutism
Hirsutism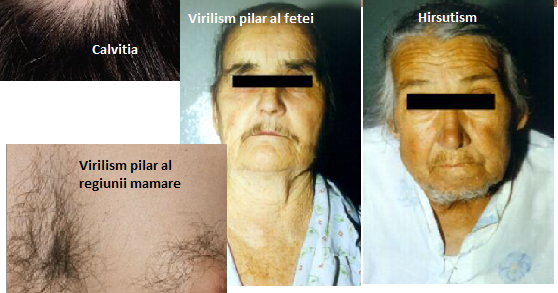 virilism
virilism
Hypercalcemia: causes
MD PIMPS ME:
- Malignancy
- Diuretics (thiazide the main culprit)
- Parathyroid (hyperparathyroidism)
- Immobilization/ Idiopathic
- Megadoses of vitamins A,D
- Paget's disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Milk alkali syndrome
- Endocrine (Addison's disease, thyrotoxicosis)

Hypercalcemia: causes
GRIM FED:
- Granulomas (sarcoid, TB),
- Renal faliure
- Immobility (esp. long term)
- Malignancy
- Familial (eg familial hypocalciuric hypercalcemia)
- Endocrine (see below for subtypes)
- Drugs (esp. thiazide diuretics, lithium)
*Endocrine causes are PATH:
- Phaeochromocytoma
- Addison's disease
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Hyperparathyroidism
Hypercalcemia: differential
VITAMIN TRAPS:
- Vitamin A and D intoxication
- Immobilization
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Addison's disease/ Acidosis
- Milk-alkali syndrome
- Inflammatory disorders
- Neoplastic disease
- Thiazides, other drugs
- Rhabdomyolysis
- AIDS
- Paget's disease/ Parenteral nutrition/ Parathyroid disease
- Sarcoidosis
Hypercalcemia: symptoms of elevated serum levels
"Bones, Stones, Groans, Moans":
- Bones: pain in bones
- Stones: renal
- Groans: pain
- Psychic moans/ Psychological overtones: confused state
Hyperthyroidism: signs and symptoms
THYROIDISM:
- Tremor
- Heart rate up
- Yawning [fatigability]
- Restlessness
- Oligomenorrhea & amenorrhea
- Intolerance to heat
- Diarrhea
- Irritability
- Sweating
- Musle wasting & weight loss
Hypothyroidism/thyroiditis: maifestations and morphology
"A SCHISM among the Axis during WWII":
- Addison disease
- Subacute thyroiditis
- Cretinism/ Cold intolerance/ Constipation
- Hashimoto's disease
- Infectious-subacute thyroiditis
- Silent thyroiditis
- Myxedema coma
*The Axis: Schimidt syndrome (when other endocrinology disorders accompany Hashimoto's disease) and "Hitler cells" (Hurthle cells, which are follicular epithelial cells with basophilic inculsions)
LH vs FSH: function in male
- LH: Leydig cells stimulated to produce testosterone.
- FSH: Spermatogenesis stimulated.
MEN I (Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia) syndrome: components
"Please Please Pay Attention To peptic ulceration, you worms":
*Adenomas of:
- Pituatary
- Pancreatic islets
- Parathyroid
- Adrenal cortex
- Thyroid, associated with peptic ulceration
*Syndrome is called "Wermer's syndrome".

Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) subtype classification
- Each subtype has 2 or 3 causes, plus something 1 or 2 more items.
- MEN I is disease of 3 P's: [Pituitary, Parathyroid, Pancreas] plus one more: adrenal cortex.
- MEN II is disease of 2 C's: [Carcinoma of thyroid, Catacholamines (pheochromocytoma)] plus two more: parathyroid for MEN IIa or
mucocutaneous neuromas for MEN IIB (also called MEN III).
Multiple endocrine neoplasia III: components
MEN III is a disease of 3 M's:
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma
- Medulla of adrenal (pheochromocytoma)
- Mucosal neuroma
Oestrogen: functions
OESTROGEN SUX:
- Organ development (sex organs)
- Endocrine: FSH and LH regulation
- Secondary sex characteristics development
- Tropic for pregnancy
- Receptor synthesis (of progesterone, oestrogen, LH)
- Osteoporosis decrease (inhibits bone reabsorption)
- Granulosa cell development
- Endocrine: increases prolactin secretion, but then blocks its effect
- Nipple development
- Sex drive increase
- Uterine contractility increase
- oXytocin sensitivity increase
Oxytocin-producing nucleus of hypothalamus
- Paraventricular nucleus--> Parturition (childbirth is oxytocin's most important role).
Pheochromocytoma: common symptoms
5 P's:
- Paroxysmal rise in BP
- Palpitations
- Perspiration
- Pain in abdomen
- PMV in urine
Pheochromocytoma: diagnositc rule
*Rule of 10's:
- 10% ectopic
- 10% multiple
- 10% malignant
Pheochromocytoma: 3 most common symptoms
"PHEochromocytoma":
- Palpitations
- Headache
- Edisodic sweating (diaphoresis)
Pituitary hormones
FLAG TOP:
- Follicle stimulating hormone
- Lutinizing hormone
- Adrenocorticotropin hormone
- Growth hormone
- Thyroid stimulating hormone
- Oxytocin
- Prolactin
Alternatively: GOAT FLAP with the second 'A' for Anti-diruetic homone/vasopressin
*Note: there is also melanocyte secreting homone and Lipotropin, but they are not well understood.
Pituitary: anterior hypophysis hormones
FLAT P wave:
- FSH
- LH
- ACTH
- TSH
- Prolactin
Progesterone: actions
PROGESTE:
- Produce cervical mucous
- Relax uterine smooth muscle
- Oxycotin sensitivity down
- Gonadotropin [FSH, LH] secretions down
- Endometrial spiral arteries and secretions up
- Sustain pregnancy
- Temperature up / Tit development
- Excitability of myometrium down
Prolactin and oxytocin: functions
- PROlactin stimulates the mammary glands to PROduce milk.
- Oxytocin stimulates the mammary glands to Ooze (release) milk.
SIADH: causes
SIADH:
- Surgery
- Intracranial: infection, head injury, CVA
- Alveolar: Ca, pus
- Drugs: opiates,antiepileptics, cytotoxics, anti-psychotics
- Hormonal: hypothyroid, low corticosteroid level
SIADH: diagnostic sign
Syndrome of INAPPropriate Anti-Diuretic Hormone:
- Increased
- Na (sodium)
- PP (urine)
*SIADH is characterized by increased urinary sodium.
SIADH: major signs and symptoms
SIADH:
- Spasms
- Isn't any pitting edema (key DDx)
- Anorexia
- Disorientation (and other psychoses)
- Hyponatremia
Sex hormone drugs: male
"Feminine Males Need Testosterone":
- Fluoxymesterone
- Methyltestosterone
- Nandrolone
- Testosterone

SIADH-inducing drugs
ABCD:
- Analgesics: opioids, NSAIDs
- Barbiturates
- Cyclophosphamide/ Chlorpromazine/ Carbamazepine
- Diuretic (thiazide)
Steroid: side effects
CUSHINGOID:
- Cataracts
- Ulcers
- Skin: striae, thinning, bruising
- Hypertension/ Hirsutism/ Hyperglycemia
- Infections
- Necrosis, avascular necrosis of the femoral head
- Glycosuria
- Osteoporosis, obesity
- Immunosuppression
- Diabetes
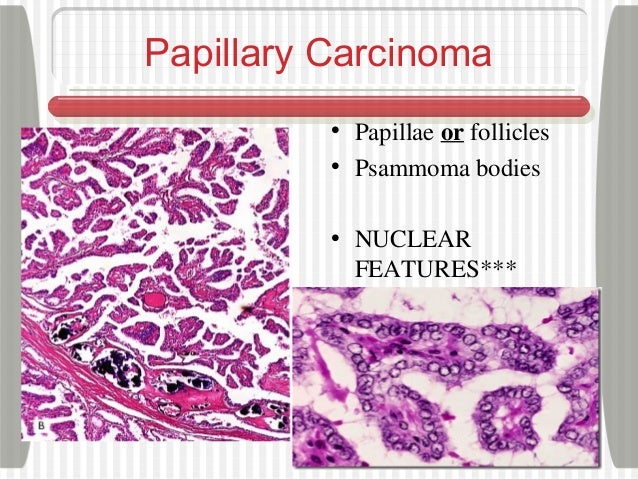
Thyroid carcinoma: features, prognosis of most popular
Most Popular is Papillary.
*Clinical features:
- Papillae (branching)
- Palpable lymph nodes
- "Pupil" nuclei (Orphan Annie)
- Psammoma bodies within lesion (often)
*Also, has a Positive Prognosis (10 year survival rate: 98%).
ENDOCRINOLOGY-Acromegaly: symptoms
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:









No comments