CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGYMNEMONICS
1. CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGYMNEMONICS
Heart compensatory mechanisms that 'save' organ blood flow during shock
"Heart SAVER":
- Sympathoadrenal system
- Atrial natriuretic factor
- Vasopressin
- Endogenous digitalis-like factor
- Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system
Heart: tropic definitions
- Lusitropic: loose is relaxed. Definition: relax heart.
- Inotropic: when heart wall contracts, moves inward. Definition: contract heart.
- Chronotropic: 'chrono-' means 'time'. Defintion: heart rate (of SA node impulses).
- Dromotropic: only one left, it must be conduction speed by default.
Heart valves: closure sequence
"Many Things Are Possible":
- Mitral, Tricuspid, Aortic, Pulmonic
Heart valves: sequence of flow
TRIPS BIAS:
- TRIcuspid
- Pulmonary
- Semilunar
- BIcuspid
- Aortic
- Semilunar
JVP: wave form
ASK ME:
- Atrial contraction
- Systole (ventricular contraction)
- Klosure (closure) of tricusps, so atrial filling
- Maximal atrial filling
- Emptying of atrium
Sino-atrial node: innervation
- Sympathetic acts on Sodium channels (SS).
- Parasympathetic acts on Potassium channels (PS).
2. CARDIAC PATHOLOGYMNEMONICS
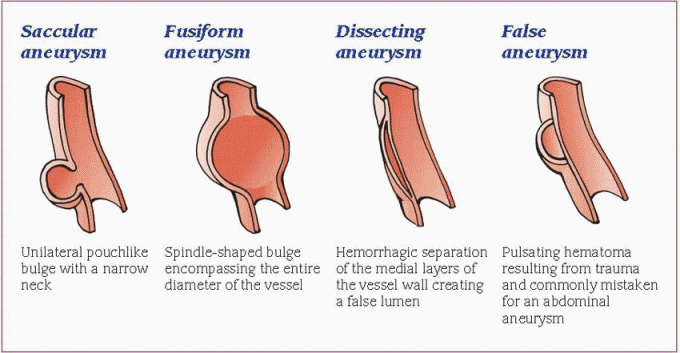
Aneurysm: types
MAD SCAB:
- Mycotic
- Atherosclerotic
- Dissecting
- Syphilitic
- Capillary microaneurysm
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Berry
Aortic regurgitation: causes
CREAM:
- Congenital
- Rheumatic damage
- Endocarditis
- Aortic dissection/ Aortic root dilatation
- Marfan Syndrome
Aortic stenosis: characteristics
SAD:
- Syncope
- Angina
- Dyspnea
Apex beat: abnormalities found on palpation, causes of impalpable
HILT:
- Heaving
- Impalpable
- Laterally displaced
- Thrusting/ Tapping
*If it is impalpable, causes are COPD:
- COPD
- Obesity
- Pleural, Pericardial effusion
- Dextrocardia
Apex beat: differential for impalpable apex beat
DOPES:
- Dextrocardia
- Obesity
- Pericarditis/ Pericardial tamponade/ Pneumothorax
- Emphysema
- Situs inversus/ Student incompetence/ Scoliosis/ Skeletal abnormalities (eg. pectus excavatum)

Atherosclerosis: risk factors
"You're a SAD BET with these risk factors":
- Sex: male
- Age: middle-aged, elderly
- Diabetes mellitus
- BP high: hypertension
- Elevated cholesterol
- Tobacco
Beck's triad (cardiac tamponade)
3 D's:
- Distant heart sounds
- Distended jugular veins
- Decreased arterial pressure
Cardiovascular: risk factors
FLASH BODIES:
- Family history
- Lipids
- Age
- Sex
- Homocystinemia
- Blood pressure
- Obesity
- Diabetes mellitus
- Inflammation (raised CRP)/ Increased thrombosis
- Exercise
- Smoking
CHF: causes of exacerbation
FAILURE:
- Forgot medication
- Arrhythmia/ Anemia
- Ischemia/ Infarction/ Infection
- Lifestyle: taken too much salt
- Up regulation of CO: pregnancy, hyperthyroidism
- Renal failure
- Embolism: pulmonary
CHF: causes of exacerbation
A SMITH PEAR:
- Anemia
- Salt/ Stress/ Stopping meds
- MI
- Infection/ Ischemia
- Thyroid (high/low)
- HTN
- Pericarditis
- Endocarditis (valve disease)
- Arrhythmia
- Rx (beta blocker, etc)
Coronary artery bypass graft: indications
DUST:
- Depressed ventricular function
- Unstable angina
- Stenosis of the left main stem
- Triple vessel disease
Deep venous thrombosis: genetic causes
ALASCA:
- Anti thrombin III
- Leiden (Factor V)
- APC (Activated Protein C)
- S-protein deficiency
- C-protein deficiency
- Anti phospholipid antibody

Deep venous thrombosis: diagnosis
DVT:
- Dilated superficial veins/ Discoloration/ Doppler ultrasound
- Venography is gold standard
- Tenderness of Thigh and calf

Heart failure: causes
"HEART MAy DIE":
- Hypertension
- Embolism
- Anemia
- Rheumatic heart disease
- Thyrotoxicosis (incl. pregnancy)
- Myocardial infarct
- Arrythmia
- Y
- Diet & lifestyle
- Infection
- Endocarditis
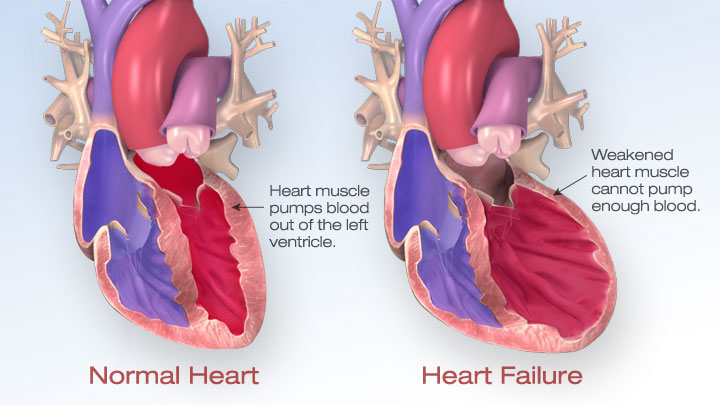
Heart failure: signs
TAPED TORCH:
- Tachycardia
- Ascites
- Pulsus alternans
- Elevated jugular venous pressure
- Displaced apex beat
- Third heart sound
- Oedema
- Right ventricular heave
- Crepitations or wheeze
- Hepatomegaly (tender)

Heart murmurs
"hARD ASS MRS. MSD":
- hARD: Aortic Regurg = Diastolic
- ASS: Aortic Stenosis = Systolic
- MRS: Mitral Regurg = Systolic
- MSD: Mitral Stenosis = Diastolic

Hypertension: secondary hypertension causes
CHAPS:
- Cushing's syndrome
- Hyperaldosteronism [aka Conn's syndrome]
- Aorta coarctation
- Phaeochromocytoma
- Stenosis of renal arteries
*Note: only 5% of hypertension cases are secondary, rest are primary.
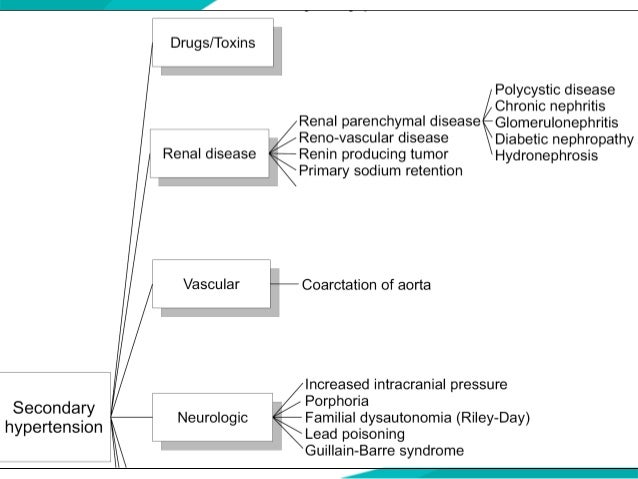
Jugular venous pressure (JVP) elevation: causes
HOLT: Grab Harold Holt around the neck and throw him in the ocean:
- Heart failure
- Obstruction of venea cava
- Lymphatic enlargement - supraclavicular
- Intra-Thoracic pressure increase

JVP: raised JVP differential
PQRST (EKG waves):
- Pericardial effusion
- Quantity of fluid raised (fluid over load)
- Right heart failure
- Superior vena caval obstruction
- Tricuspid stenosis/ Tricuspid regurgitation/ Tamponade (cardiac)
JVP: raised JVP: extra-cardiac causes
FAT PEA:
- Fever
- Anaemia
- Thyrotoxicosis
- Pregnancy
- Exercise
- A-V fistula
*These are in addition to all the cardiac ones (pericardial effusion, RHF, tricuspid stenosis, SVC obstruction, etc).
MI: complications
HAS CRAPPED:
- Heart failure/ Hypertension
- Arrhythmia
- Shock
- Cardiac Rupture
- Aneurysm
- Pericarditis
- Pulmonary Emboli
- DVT
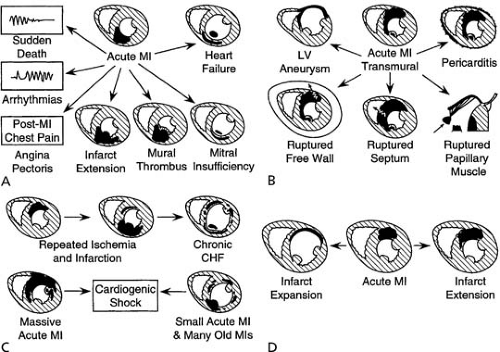
MI: complications
LEAP on the MAP
- LVF
- Embolism (systemic)
- Aneurysm (ventricular)
- Progressive infarction
- Myocardial rupture
- Arrhythmia
- Pericarditis
MI: post-MI complications
ACT RAPID:
- Arrhythmias (SVT, VT, VF)
- Congestive cardiac failure
- Tamponade/ Thromboembolic disorders
- Rupture (ventricle, septum, papillary muscle)
- Aneurysm (ventricle)
- Pericarditis
- Infaction (a second one)
- Death/ Dressler's syndrome
MI: signs and symptoms
PULSE:
- Persistent chest pains
- Upset stomach
- Lightheadedness
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive sweating
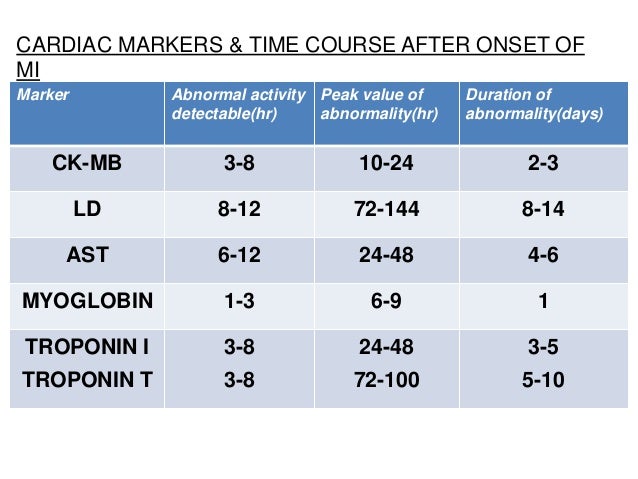
MI: sequence of elevated enzymes after MI
"Time to CALL 911":
From first to appear to last:
- Troponin
- CK-MB
- AST
- LDH1
Mitral stenosis (MS) vs. regurgitation (MR): epidemiology
- MS is a female title (Ms.) and it is female predominant.
- MR is a male title (Mr.) and it is male predominant.
Murmur attributes
IL PQRST (person has ill PQRST heart waves):
- Intensity
- Location
- Pitch
- Quality
- Radiation
- Shape
- Timing
Murmurs: innocent murmur features
8 S's:
- Soft
- Systolic
- Short
- Sounds (S1 & S2) normal
- Symptomless
- Special tests normal (X-ray, EKG)
- Standing/ Sitting (vary with position)
- Sternal depression
Murmurs: locations and descriptions
"MRS ASS":
- MRS: Mitral Regurgitation--Systolic
- ASS: Aortic Stenosis--Systolic
The other two murmurs, Mitral stenosis and Aortic regurgitation, are obviously diastolic.

Murmurs: louder with inspiration vs expiration
- LEft sided murmurs louder with Expiration
- RIght sided murmurs louder with Inspiration.
Murmurs: questions to ask
SCRIPT:
- Site
- Character (eg harsh, soft, blowing)
- Radiation
- Intensity
- Pitch
- Timing
Murmurs: right vs. left loudness
"RILE":
- Right sided heart murmurs are louder on Inspiration.
- Left sided heart murmurs are loudest on Expiration.
Murmurs: systolic
MR PV TRAPS:
- Mitral
- Regurgitation and
- Prolaspe
- VSD
- Tricupsid
- Regurgitation
- Aortic and
- Pulmonary
- Stenosis
Murmurs: systolic types
SAPS:
- Systolic
- Aortic
- Pulmonic
- Stenosis
Systolic murmurs include aortic and pulmonary stenosis. Similarly, it's common sense that if it is aortic and pulmonary stenosis it could also be mitral and tricuspid regurgitation.
Murmurs: systolic vs. diastolic
- PASS: Pulmonic & Aortic Stenosis=Systolic.
- PAID: Pulmonic & Aortic Insufficiency=Diastolic.

Pericarditis: causes
CARDIAC RIND:
- Collagen vascular disease
- Aortic aneurysm
- Radiation
- Drugs (such as hydralazine)
- Infections
- Acute renal failure
- Cardiac infarction
- Rheumatic fever
- Injury
- Neoplasms
- Dressler's syndrome
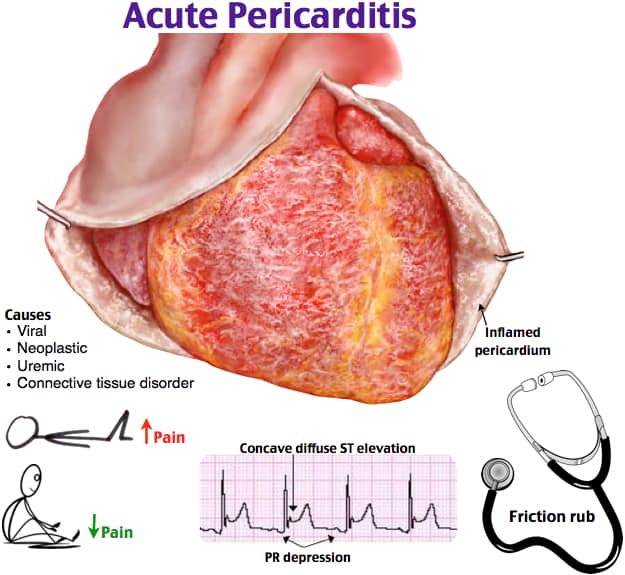
Pericarditis: findings
PERICarditis:
- Pulsus paradoxus
- ECG changes
- Rub
- Increased JVP
- Chest pain [worse on inspiration, better when lean forward]
Peripheral vascular insufficiency: inspection criteria
DISC V:
- Distribution of hair
- Integrity of skin
- Symmetry of leg musculature
- Color of toenails
- Varicose veins
Rheumatic fever: Revised Jones criteria
JONES PEACE:
*Major criteria: (JONES)
- Joints: migratory
- O (heart shaped) Carditis: new onset murmur
- Nodules, subcutaneous: extensor surfaces
- Erythema marginatum
- Sydenham's chorea
*Minor criteria: (PEACE)
- PR interval, prolonged
- ESR elevated
- Arthralgias
- CRP elevated
- Elevated temperature (fever)
Need 2 major or 1 major and 2 minor criteria, plus evidence of recent GAS infection (throat cx, rapid antigen test, or rising strep antibody titer).
Rheumatic fever: Revised Jones' criteria
JONES crITERIA:
*Major criteria: (JONES)
- Joint (arthritis)
- Obvious (Cardiac)
- Nodule (Rheumatic)
- Erythema marginatum
- Sydenham chorea
*Minor criteria: (crITERIA)
- Inflammatory cells (leukocytosis)
- Temperature (fever)
- ESR/CRP elevated
- Raised PR interval
- Itself (previous Hx of Rheumatic fever)
- Arthralgia
Shock: general features
CHORD ITEM:
- Cold, clammy skin
- Hypotension
- Oliguria
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Drowsiness, confusion
- Irritability
- Tachycardia
- Elevated or reduced central venous pressure
- Multi-organ damage
Syncope causes, by system:
HEAD, HEART & VESSELS:
CNS causes include: (HEAD):
- Hypoxia/ Hypoglycemia
- Epilepsy
- Anxiety
- Dysfunctional brain stem (basivertebral TIA)
Cardiac causes are: (HEART)
- Heart attack
- Embolism (PE)
- Aortic obstruction (IHSS, AS or myxoma)
- Rhythm disturbance, ventricular
- Tachycardia
Vascular causes are : VESSELS
- Vasovagal
- Ectopic (reminds one of hypovolemia)
- Situational
- Subclavian steal
- ENT (glossopharyngeal neuralgia)
- Low systemic vascul
- Sensitive carotid sinus

3. CARDIAC PHARMACOLOGYMNEMONICS
ACEI: Contraindications
PARK:
- Pregnancy
- Allergy
- Renal artery stenosis
- K increase (hyperkalemia)
Anti- arrhythmics (classification I to IV ):
MBA College
In order of class I to IV:
- Membrane stabilizers (class I)
- Beta blockers
- Action potential widening agents
- Calcium channel blockers
Anti- arrhythmics: class III members
BIAS:
- Bretylium
- Ibutilide
- Amiodarone
- Sotalol
Anti-arrythmics: for AV nodes
Do Block AV":
- Digoxin
- B-blockers
- Adenosine
- Verapamil
Asprin: side effects
ASPRIN
- Aplastic anemia
- Salt & water retention
- Peptic ulcer
- Rash (skin Rash)
- Induce bronchial asthma
- Nephrotoxicity
Beta blockers: cardio selective beta blockers
"Beta blockers Acting Exclusively At Myocardium"
Cardio selective beta blockers are:
- Betaxolol
- Acebutelol
- Esmolol
- Atenolol
- Metoprolol

Beta-blockers: main contraindications, cautions
ABCDE:
- Asthma
- Block (heart block)
- COPD
- Diabetes mellitus
- Electrolyte (hyperkalemia)
Beta-blockers: side effects
"BBC Loses Viewers In Rochedale":
- Bradycardia
- Bronchoconstriction
- Claudication
- Lipids
- Vivid dreams & nightmares
- -ve Inotropic action
- Reduced sensitivity to hypoglycaemia
Captopril (an ACE inhibitor): side effects
CAPTOPRIL:
- Cough
- Angioedema/ Agranulocystosis
- Proteinuria/ Potassium excess
- Taste changes
- Orthostatic hypotension
- Pregnancy contraindication/ Pancreatitis/ Pressure drop (first dose hypertension)
- Renal failure (and renal artery stenosis contraindication)/ Rash
- Indomethacin inhibition
- Leukopenia/ Liver toxicity
Ca++ channel blockers: uses
CA++ MASH:
- Cerebral vasospasm/ CHF
- Angina
- Migraines
- Atrial flutter, fibrillation
- Supraventricular tachycardia
- Hypertension
*Alternatively: "CHASM":
- Cerebral vasospasm / CHF
- Hypertension
- Angina
- Supraventricular tachyarrhythmia
- Migraines

Hypertension: treatment
ABCD:
- ACE inhibitors/ AngII antagonists (sometimes Alpha agonists also)
- Beta blockers
- Calcium antagonists
- Diuretics

MI: basic management
BOOMAR:
- Bed rest
- Oxygen
- Opiate
- Monitor
- Anticoagulate
- Reduce clot size
Myocardial infarctions: treatment
INFARCTIONS:
- IV access
- Narcotic analgesics (eg morphine, pethidine)
- Facilities for defibrillation (DF)
- Aspirin/ Anticoagulant (heparin)
- Rest
- Converting enzyme inhibitor
- Thrombolysis
- IV beta blocker
- Oxygen 60%
- Nitrates
- Stool Softeners
Pulmonary edema: treatment
LMNOP:
- Lasix
- Morphine
- Nitrates (NTG)
- Oxygen
- Position (upright vs. flat)
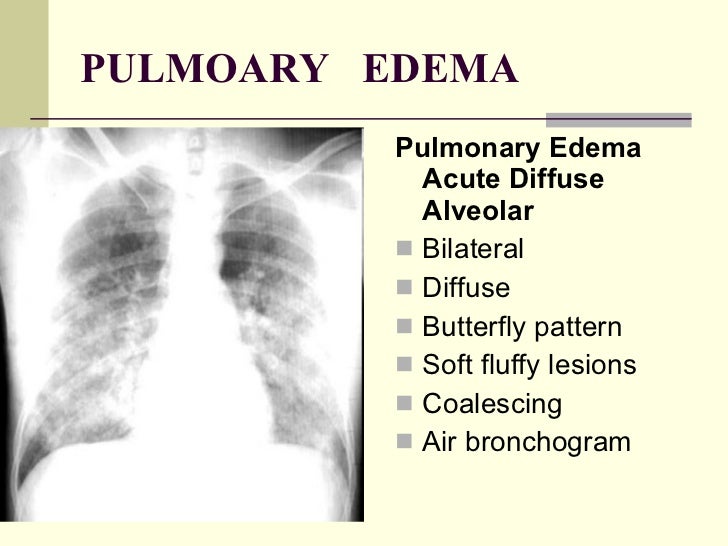
Pulmonary edema: treatments
MAD DOG:
- Morphine
- Aminophylline
- Digitalis
- Diuretics
- Oxygen
- GGases in blood (ABG's)
Thrombolytic agents
USA:
- Urokinase
- Streptokinase
- Alteplase (Tissue Plasminogen Activator)

4. ECG MNEMONICS
Atrial fibrillation: causes of new onset
THE ATRIAL FIBS:
- Thyroid
- Hypothermia
- Embolism (P.E.)
- Alcohol
- Trauma (cardiac contusion)
- Recent surgery (post CABG)
- Ischemia
- Atrial enlargement
- Lone or idiopathic
- Fever, anemia, high-output states
- Infarct
- Bad valves (mitral stenosis)
- Stimulants (cocaine, theo,amphet, caffeine)

Atrial fibrillation: causes
PIRATES:
- Pulmonary: PE, COPD
- Iatrogenic
- Rheumatic heart: mirtral regurgitation
- Atherosclerotic: MI, CAD
- Thyroid: hyperthyroid
- Endocarditis
- Sick sinus syndrome
Atrial fibrillation: management
ABCD:
- Anti-coagulate
- Beta-block to control rate
- Cardiovert
- Digoxin
Depressed ST-segment: causes
DEPRESSED ST:
- Drooping valve (MVP)
- Enlargement of LV with strain
- Potassium loss (hypokalemia)
- Reciprocal ST- depression (in I/W AMI)
- Embolism in lungs (pulmonary embolism)
- Subendocardial ischemia
- Subendocardial infarct
- Encephalon hemorrhage (intracranial hemorrhage)
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
- Shock
- Toxicity of digitalis, quinidine
Exercise ramp ECG: contraindications
RAMP:
- Recent MI
- Aortic stenosis
- MI in the last 7 days
- Pulmonary hypertension
ECG: left vs. right bundle block
"WiLLiaM MaRRoW":
- W pattern in V1-V2 and M pattern in V3-V6 is Left bundle block.
- M pattern in V1-V2 and W in V3-V6 is Right bundle block.

ECG: T wave inversion causes
INVERT:
- Ischemia
- Normality [esp. young, black]
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Ectopic foci [eg calcified plaques]
- RBBB, LBBB
- Treatments [digoxin]


Pericarditis: EKG
"PericarditiS":
- PR depression in precordial leads.
- ST elevation.
Pulseless electrical activity: causes
PATCH MED:
- Pulmonary embolus
- Acidosis
- Tension pneumothorax
- Cardiac tamponade
- Hypokalemia/ Hyperkalemia/ Hypoxia/ Hypothermia/ Hypovolemia
- Myocardial infarction
- Electrolyte derangements
- Drugs

Sinus bradycardia: Etiology
"SINUS BRADICARDIA" (sinus bradycardia):
- Sleep
- Infections (myocarditis)
- Neap thyroid (hypothyroid)
- Unconsciousness (vasovagal syncope)
- Subnormal temperatures (hypothermia)
- Biliary obstruction
- Raised CO2 (hypercapnia)
- Acidosis
- Deficient blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Imbalance of electrolytes
- Cushing's reflex (raised ICP)
- Aging
- Rx (drugs, such as high-dose atropine)
- Deep anaesthesia
- Ischemic heart disease
- Athletes
Sinus tachycardia: Etiology
TACH FEVER:
- Tamponade/ Thyrotoxicosis
- Anemia
- CHF
- Hypotension
- Fever
- Excrutiating pain
- Volume depletion
- Exercise
- Rx (Theo, Dopa, Epi, etc)

ST elevation: causes in ECG
ELEVATION:
- Electrolytes
- LBBB
- Early repolarization
- Ventricular hypertrophy
- Aneurysm
- Treatment (eg. pericardiocentesis)
- Injury (AMI, contusion)
- Osborne waves (hypothermia)
- Non-occlusive vasospasm
Supraventricular tachycardia: treatment
ABCDE:
- Adenosine
- Beta-blocker
- Calcium channel antagonist
- Digoxin
- Excitation (vagal stimulation)
CARDIAC PHYSIOLOGYMNEMONICS
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:










No comments