COSTROENDEROLOGYAbdominal pain: medical causes
COSTROENDEROLOGYAbdominal pain: medical causes




































Abdominal pain: medical causes
"ABDOMENAL PANE" [abdominal pain]:
- Acute rheumatic fever
- Blood [purpura, a/c hemolytic crisis]
- DKA
- cOllagen vascular disease
- Migraine [abdominal migraine]
- Epilepsy [abdominal epilepsy]
- Nephron [uremia]
- Abdominal angina
- Lead
- Porphyria
- Arsenic
- NSAID's
- Enteric fever

Abdomen: inspection
5 S's:
- Size
- Shape
- Scars
- Skin lesions
- Stoma

Bilirubin: common causes for increased levels
"HOT Liver":
- Hemolysis
- Obstruction
- Tumor
- Liver disease
Bowel components
"David Johnson Is American Cardiac Surgery Resident":
From proximal to distal:
- Duodenum
- Jejunum
- Ileum
- Appendix
- Colon
- Sigmoid
- Rectum
Carcinoid syndrome: components
CARCinoid:
- Cutaneous flushing
- Asthmatic wheezing
- Right sided valvular heart lesions
- Cramping and diarrhea
Celiac sprue gluten sensitive enteropathy: gluten-containing grains
BROW:
- Barley
- Rye
- Oats
- Wheat
Flattened intestinal villi of celiac sprue are smooth, like an eyebrow.
Charcot's triad (gallstones)
"Charcot's Triad is 3 C's":
- Color change (jaundice)
- Colic (biliary) pain, aka RUQ pain
- Chills and fever

Charcot's triad (gallstones)
"Charge a FEE":
- Charcot's triad is:
- Fever
- Epigastric & RUQ pain
- Emesis & nausea
Cholangitis: features
CHOLANGITITS:
- Charcot's triad/ Conjugated bilirubin increase
- Hepatic abscesses/ Hepatic (intra/extra) bile ducts/ HLA B8, DR3
- Obstruction
- Leukocytosis
- Alkaline phosphatase increase
- Neoplasms
- Gallstones
- Inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis)
- Transaminase increase
- Infection
- Sclerosing
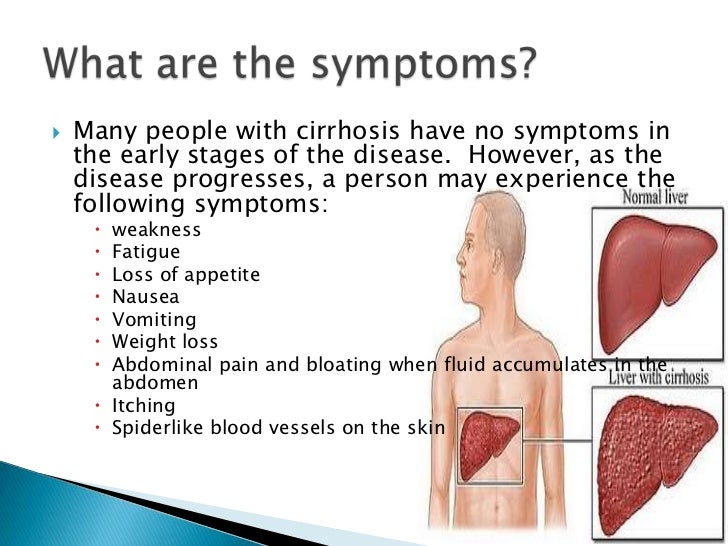
Cirrhosis: causes of hepatic cirrhosis
HEPATIC:
- Hemochromatosis (primary)
- Enzyme deficiency (alpha-1-anti-trypsin)
- Post hepatic (infection + drug induced)
- Alcoholic
- Tyrosinosis
- Indian childhood (galactosemia)
- Cardiac/ Cholestatic (biliary)/ Cancer/ Copper (Wilson's)
Cirrhosis: differential: common and rarer
Common causes are ABC:
- Alcohol
- B (Hepatitis)
- C (Hepatitis)
*Rarer are also ABC:
- Autoimmune
- Biliary cirrhosis
- Copper (Wilson's)

Constipation: causes
DOPED:
- Drugs (e.g opiates)
- Obstruction (e.g IBD, cancer)
- Pain
- Endocrine (e.g hypothyroid)
- Depression

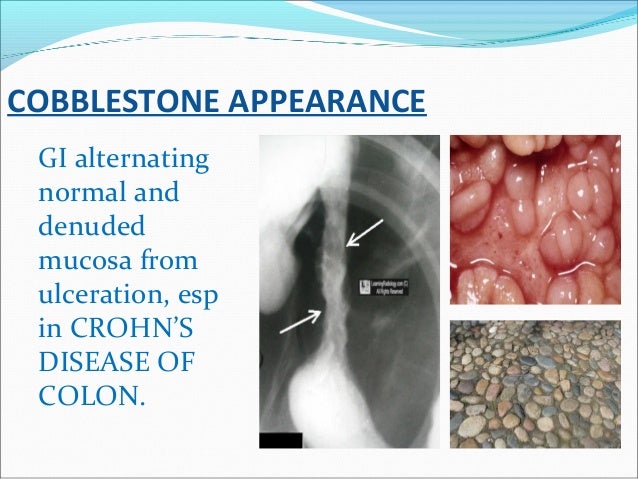
Crohn's disease: morphology, symptoms
CHRISTMAS:
- Cobblestones
- High temperature
- Reduced lumen
- Intestinal fistulae
- Skip lesions
- Transmural (all layers, may ulcerate)
- Malabsorption
- Abdominal pain
- Submucosal fibrosis
Diabetic ketoacidosis: precipitating factors
5 I's:
- Infection
- Ischaemia (cardiac, mesenteric)
- Infarction
- Ignorance (poor control)
- Intoxication (alcohol)


Digestive disorders: pH level
- With vomiting both the pH and food come up.
- With diarrhea both the pH and food go down.
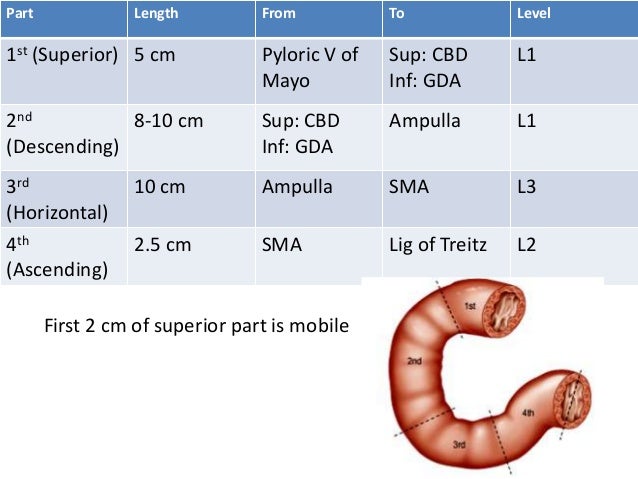
Duodenum: lengths of parts
"Counting 1 to 4 but staggered":
- 1st part: 2 inches
- 2nd part: 3 inches
- 3rd part: 4 inches
- 4th part: 1 inch

Dry mouth: differential
"DRI":
2 of each:
- Drugs/ Dehydration
- Renal failure/ Radiotherapy
- Immunological (Sjogren's)/ Intense emotions

Dysphagia: causes
MOON:
- Mouth lesions
- Obstruction
- Oesophageal stricture
- Neurological (eg stroke, Guillain-Barre, achalasia)

Dysphagia: differential
DISPHAGIA:
- Disease of mouth and tonsils/ Diffuse oesophageal spasm/ Diabetes mellitus
- Intrinsic lesion
- Scleroderma
- Pharyngeal disorders/ Palsy-bulbar-MND
- Achalasia
- Heart: eft atrium enlargement
- Goitre/ myesthenia Gravis/ mediastinal Glands
- Infections
- American trypanosomiasis (chagas disease)
Esophageal cancer: risk factors
ABCDEF:
- Achalasia
- Barret's esophagus
- Corrosive esophagitis
- Diverticuliis
- Esophageal web
- Familial

Gallstones: risk factors
5 F's:
- Fat
- Female
- Family history
- Fertile
- Forty
GIT symptoms:
BAD ANAL SHIT:
- Bleeding
- Abdominal pain
- Dysphagia
- Abdominal bloating
- Nausea & vomiting
- Anorexia/ Appetite changes
- Lethargy
- Shits (diarrhea)
- Heartburn
- Increased bilirubin (jaundice)
- Temperature (fever)

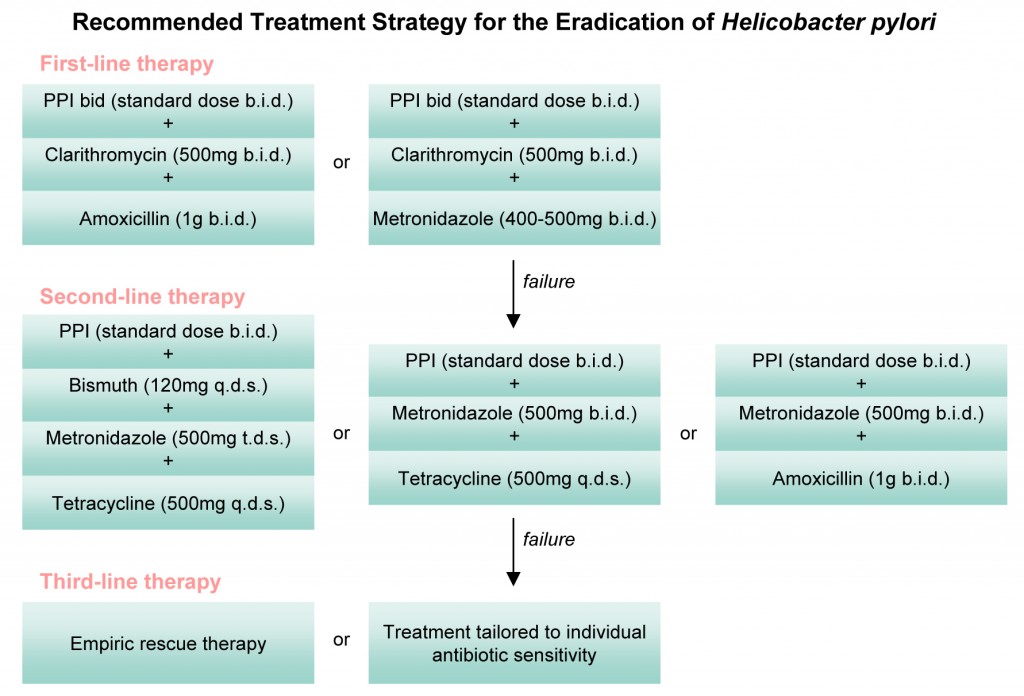
H. Pylori treatment regimen (rough guidelines)
"Please Make Tummy Better":
- Proton pump inhibitor
- Metronidazole
- Tetracycline
- Bismuth
Alternatively: TOMB:
- Tetracycline
- Omeprazole
- Metronidazole
- Bismuth

Haemochromatosis: definition, classic triad
"Iron man triathalon":
- Iron man: deposition of iron in many body tissues.
- Triathalon has 3 components, which match triad:
- Swimming: Skin pigmentation
- Biking: Bronze diabetes
- Marathon: Micronodular pigment cirrhosis
Haemachromatosis : complications
"HaemoChromatosis Can Cause Deposits Anywhere":
- Hypogonadism
- Cancer (hepatocellular)
- Cirrhosis
- Cardiomyopathy
- Diabetes mellitus
- Arthropathy

Hepatic encephalopathy: precipitating factors
HEPATICS:
- Hemorrhage in GIT/ Hyperkalemia
- Excess protein in diet
- Paracentesis
- Acidosis/ Anemia
- Trauma
- Infection
- Colon surgery
- Sedatives
Hepatic necrosis: drugs causing focal to massive necrosis
"Very Angry Hepatocytes":
- Valproic acid
- Acetaminophen
- Halothane
Hepatocellular carcinoma: aetiology, features
ABC
- Aflatoxins
- Hep B
- Cirrhosis
*Features:
- AFP increased (classic marker)
- Bile-producing (DDx from cholangiocarcinoma)
- Commonest primary liver tumor
Hepatomegaly: 3 common causes, 3 rarer causes
Common are 3 C's:
- Cirrhosis
- Carcinoma
- Cardiac failure
*Rarer are 3 C's:
- Cholestasis
- Cysts
- Cellular infiltration

Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer (HNPCC) cause:
is DNA mismatch repair
- DNA mismatch causes a bubble in the strand where the two nucleotides don't match.
- This looks like the ensuing polyps that arise in the colon.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease: which has cobblestones
- Crohn's has Cobblestones on endoscopy.

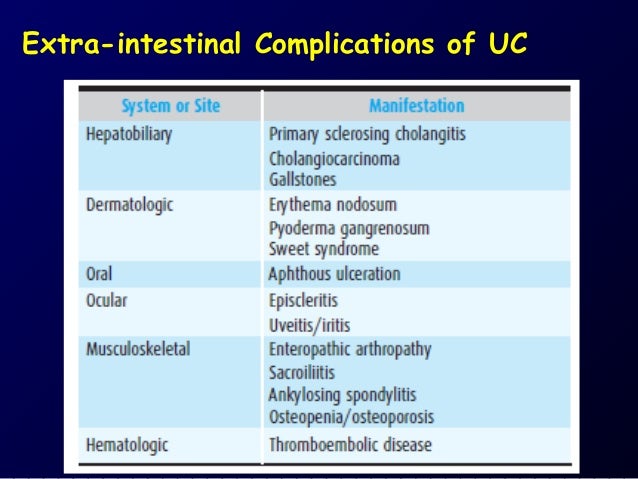
IBD: extraintestinal manifestations
A PIE SAC:
- Aphthous ulcers
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Iritis
- Erythema nodosum
- Sclerosing cholangitis
- Arthritis
- Clubbing of fingertips
IBD: surgery indications
"I CHOP":
- Infection
- Carcinoma
- Haemorrhage
- Obstruction
- Perforation
"Chop" convenient since surgery chops them open.
Ileus: causes
MD SPUGERS:
- Mesenteric ischemia
- Drugs (see below)
- Surgical (post-op)
- Peritonitis/ Pancreatitis (sentinnel loop)
- Unresolved mechanical obstruction (eg mass, intussusception, blockage)
- Gram negative sepsis
- Electrolyte imbalance (eg hypokalemia)
- Retroperitoneal bleed or hematoma
- Spinal or pelvic fracture
Drugs are Aluminum hydroxide, Ba++, Ca carbonate, opiates, TCA, verapamil.

Left iliac fossa: causes of pain
SUPER CLOT:
- Sigmoid diverticulitis
- Uteric colic
- PID
- Ectopic pregnancy
- Rectus sheath haematoma
- Colorectal carcinoma
- Left sided lower love pneumonia
- Ovarian cyst (rupture, torture)
- Threatened abortion/ Testicular torsion
Liver failure: decompensating chronic liver failure differential
HEPATICUS:
- Haemorrhage
- Electrolyte disturbance
- Protein load/ Paracetamol
- Alcohol binge
- Trauma
- Infection
- Constipation
- Uraemia
- Sedatives/ Shunt/ Surgery
Liver failure (chronic): signs found on the arms
CLAPS:
- Clubbing
- Leukonychia
- Asterixis
- Palmar erythema
- Scratch marks
Pancreatitis: causes
PANCREATITIS:
- Posterior
- Alcohol
- Neoplasm
- Cholelithiasis
- Rx (lasix, AZT)
- ERCP
- Abdominal surgery
- Trauma
- Infection (mumps)
- Triglycerides elevated
- Idiopathic
- Scorpion bite
Pancreatitis: criteria
PANCREAS:
- PaO2 below 8
- Age >55
- Neutrophils: WCC >15
- Calcium below 2
- Renal: Urea >16
- Enzymes: LDH >600; AST >200
- Albumin below 32
- Sugar: Glucose >10 (unless diabetic patient)
Pancreatitis: Ranson criteria for pancreatitis at admission
LEGAL:
- Leukocytes > 16000
- Enzyme AST > 250
- Glucose > 200
- Age > 55
- LDH > 350
Pancreatitis: Ranson criteria for pancreatitis: initial 48 hours
"C & HOBBS" (Calvin and Hobbes):
- Calcium < 8
- Hct drop > 10%
- Oxygen < 60 mm
- BUN > 5
- Base deficit > 4
- Sequestration of fluid > 6L
Peptic ulcer: associated causative factors
SHAZAM:
- Smoking
- Hypercalcemia
- Aspirin
- Zollinger-Ellison
- Acidity
- MEN type I
These may work with H. pylori to promote ulceration, or may act alone.


Portal hypertension: features
ABCDE:
- Ascites
- Bleeding (haematemesis, piles)
- Caput medusae
- Diminished liver
- Enlarged spleen
RLQ pain: differential
APPENDICITIS:
- Appendicitis/ Abscess
- PID/ Period
- Pancreatitis
- Ectopic/ Endometriosis
- Neoplasia
- Diverticulitis
- Intussusception
- Crohns Disease/ Cyst (ovarian)
- IBD
- Torsion (ovary)
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- Stones

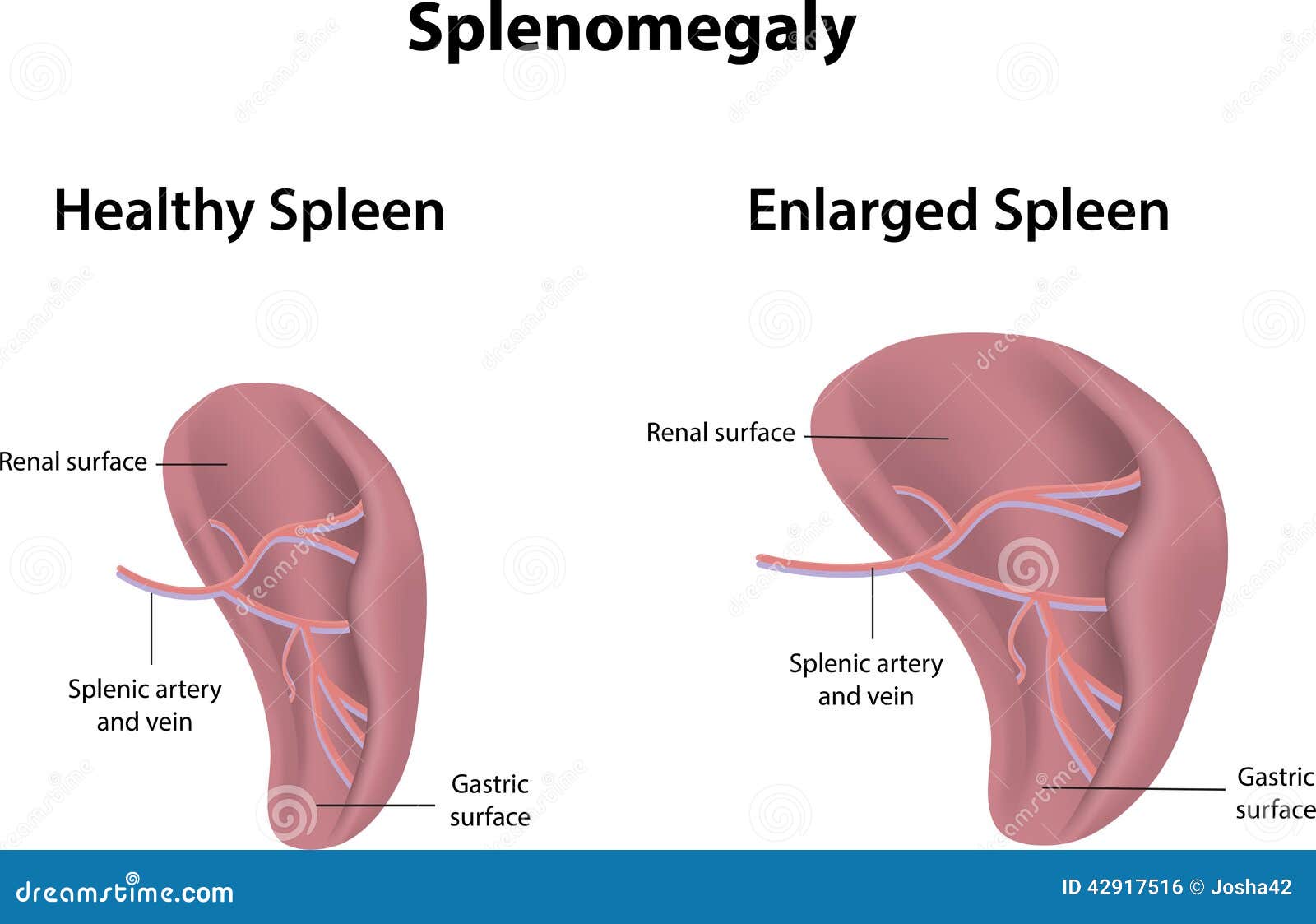
Spleen: dimensions, weight, surface anatomy
"1,3,5,7,9,11":
- Spleen dimensions are 1 inch x 3 inches x 5 inches.
- Weight is 7 ounces.
- It underlies ribs 9 through 11.

Splenomegaly: causes
CHICAGO:
- Cancer
- Hem, onc
- Infection
- Congestion (portal hypertension)
- Autoimmune (RA, SLE)
- Glycogen storage disorders
- Other (amyloidosis)

Splenomegaly: causes
HICCUPS:
- Haematological
- Infective : Kala azar, malaria, enteric fever
- Congestive: CCF, constrictive pericarditis, IVC thrombosis, Hepatic vein thrombosis, portal vein thrombosis and splenic vein thrombosis
- Collagen diseases: SLE, Felty's syndrome
- Unknown etiology: tropical splenomegaly
- Primary malignacies (secondaries are rare)
- Storage diseases: Gaucher's disease, Niemman Pick

Ulcerative colitis: definition of a severe attack
A STATE:
- Anemia less than 10g/dl
- Stool frequency greater than 6 stools/day with blood
- Temperature greater than 37.5
- Albumin less than 30g/L
- Tachycardia greater than 90bpm
- ESR greater than 30mm/hr
Ulcerative colitis: complications
"PAST Colitis":
- Pyoderma gangrenosum
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Sclerosing pericholangitis
- Toxic megacolon
- Colon carcinoma

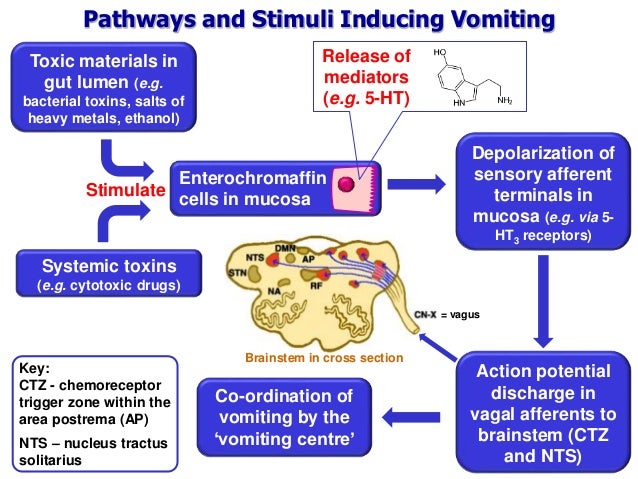
Vomiting: extra GI differential
VOMITING:
- Vestibular disturbance/ Vagal (reflex pain)
- Opiates
- Migrane/ Metabolic (DKA, gastroparesis, hypercalcemia)
- Infections
- Toxicity (cytotoxic, digitalis toxicity)
- Increased ICP, Ingested alcohol
- Neurogenic, psychogenic
- Gestation


Whipple's disease: clinical manifestations
SHELDA:
- Serositis
- Hyperpigmentation of skin
- Eating less (weight loss)
- Lymphadenopathy
- Diarrhea
- Arthritis
- sss

COSTROENDEROLOGYAbdominal pain: medical causes
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 05, 2018
Rating:










No comments