Alzheimer's disease (AD):
Alzheimer's disease (AD): associations, findings
AD:
*Associations:
- Aluminum toxicity
- Acetylcholine deficiencies
- Amyloid B
- Apolipoprotein gene E
- Altered nucleus basalis of Meynert
- Down's
*Findings:
- Actin inclusions (Hirano bodies)
- Atrophy of brain
- Amyloid plaques
- Aphasia, Apraxia, Agitation
- DNA-coiled tangles
- Dementia, Disoriented, Depressed

Alzheimer's disease: common characteristics
ALZHEIMER'S:
- Anterograde amnesia is usually first sign
- Life expectancy increase shows more cases in recent years
- Zapped (loss of) acetylcholinergic neurons
- Hereditary disease
- Entire hippocampus becomes affected
- Identified by neurofibrillary tangles
- Mutation in amyloid genes associated w/ disease
- Entorhinal areas degenerate first
- Retrograde amnesia ultimaltely develops
- Senile plaques are formed at synapse
Argyll-Robertson Pupil: features
- Argyll Robertson Pupil (ARP)
- Read it from front to back: it is ARP, standing for Accomodation Reflex Present.
- Read it from back to front: it is PRA, standing for Pupillary Reflex Absent.
Argyll-Robertson Pupil: features
- Argyll Robertson Pupil is like a prostitute.
- She/he will accomodate, but will not react.
*Pupil still accomodates, but doesn't react to light.
*Pupil is a common sign in syphilis, which is often carried by prostitutes.

Auditory pathway: mandatory stops
"Come In My Baritone":
- Cochlear nucleus
- Inferior colliculus
- Medial geniculate nucleus
- Brodmann's 41 (cortex)
Babinski and LMN signs: conditions exhibiting them
"D MASTS":
- Diabetes
- Motor neuron disease
- Ataxia (friedrichs)
- Subacute combined degeneration of cord
- Tabo paresis
- Syringobulbia

Balint's syndrome
SOOT:
- Simultagnosia
- Optic ataxia
- Ocular apraxia
- Tunnel vision
Basal ganglia: D1 vs. D2 connections
- D1 has 1 connection (Striatum-GPi/SNpr).
- D2 has 2 connections (Striatum-GPe-GPi/SNpr).
Basal ganglia: indirect vs. direct pathway
- The Indirect pathway Inhibits.
- Direct pathway is hence the excitatory one.

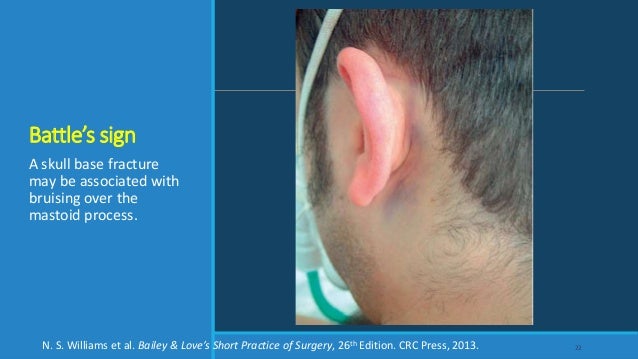
Battle sign
- BattlE:
- Behind Ear
Bell's palsy: symptoms
BELL'S Palsy:
- Blink reflex abnormal
- Earache
- Lacrimation [deficient, excess]
- Loss of taste
- Sudden onset
- Palsy of VII nerve muscles
All symptoms are unilateral.

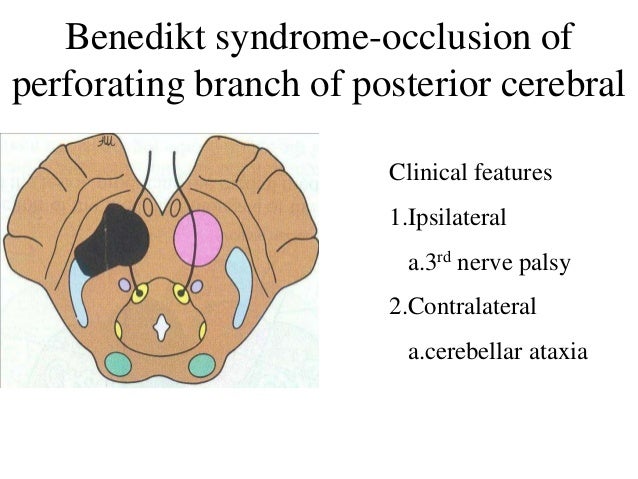
Benidict's syndrome: site affected
- Benidict's test for sugar gives red precipitate.
- Similarly, Benidict's syndrome affects red nucleus.
Branchial arches: cranial nerve innervation
In Sensory/Motor/Both mnemonic 'Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says
Big Boobs Matter More', the B's also give Brancial arch
nerves in order:
- But (CN 5): 1st arch
- Brother (CN7): 2nd arch
- Big (CN9): 3rd arch
- Boobs (CN 10): 4th arch
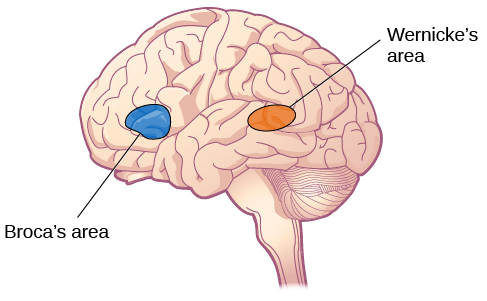
Broca's vs. Wernick's area: effect of damage to speech center
- "Broca": your speech machinery is Broken. Broca is wanting to speak, but articulation doesn't work, and very slow.
- "Wer-nick": "were" and "nick" are both words of English language, but together they are nonsensical. *Wernick is having good articulation, but saying words that don't make sense together.
Cerebellar deep nuclei
"Ladies Demand Exceptional Generosity From Men":
The 4 nuclei, from lateral to medial:
*[Lateral]
- Dentate
- Emboliform
- Globose
- Fastigial
*[Medial]
*Alternatively,
"Fat Girls Eat Doughnuts":
From medial to lateral:
- Fastigial
- Globose
- Emboliform
- Dentate
Cerebellar damage: symptoms
VANISHeD:
- Vertigo
- Ataxia
- Nystagmus
- Intention tremor
- Slurred speech
- Hypotonic reflexes
- Dysdiadochokinesia.
Cerebellar: functional areas
Anatomical shape/location of cerebellar areas is a key to their function and related tract.
Vermis = Spinocerebellar = Axial equilibrium.
Vermis: right down the axis of cerebellum, and vertically segmented like a spinal column.Flocculonodular lobe = Vestibulocerebellar = Ear, eye, body coordination.
Flocculonodular lobe: flares out to the edges, just like ears.
Hemispheres of cerebellum = Cerebrocerebellar = Peripheral coordination.
Hemispheres: around periphery of cerebellum, and tract to cerebral hemispheres.

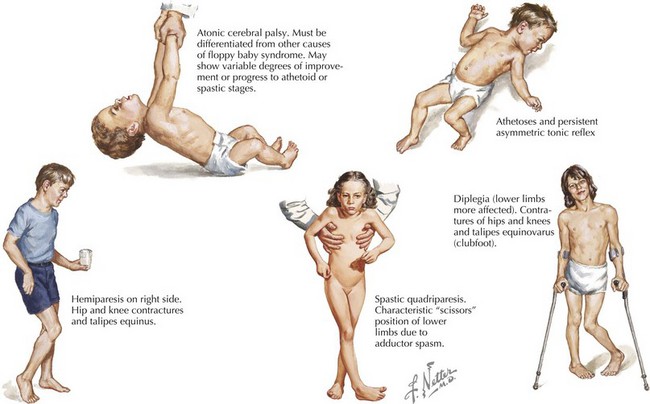
Cerebral palsy: general features
PALSY:
- Paresis
- Ataxia
- Lagging motor development
- Spasticity
- Young
Cerebellar peduncles: afferent vs efferent
SEMA:
- Superior cerebellar peduncle
- Efferent (fibres)
- Middle cerebellar peduncle
- Afferent (fibres)
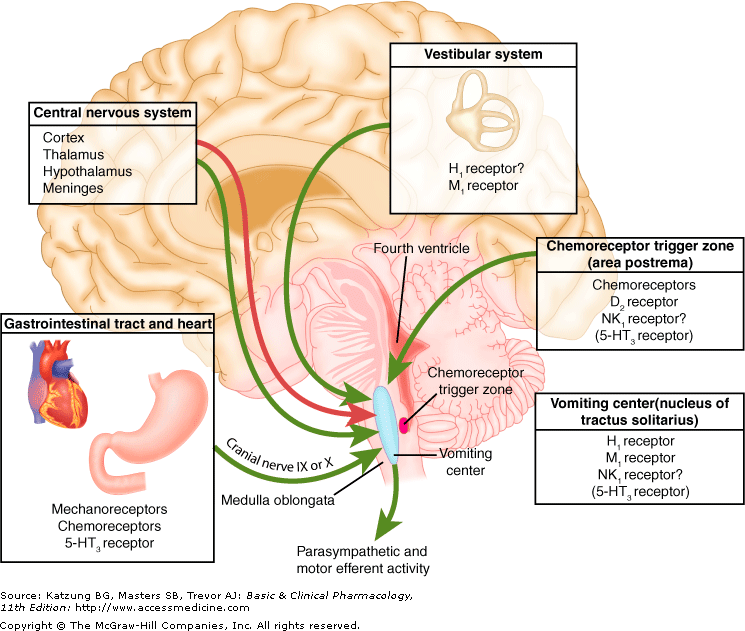
Chemoreceptor trigger zone
"Syringes Help Men On Drugs":
- Serotonin
- Histamine
- Muscarinic
- Opioids
- Dopamine
Chorea: common causes
Some VITUS'S DANCE:
- Sydenhams
- Vascular
- Increased RBC's (polycythemia)
- Toxins: CO, Mg, Hg
- Uremia
- SLE
- Senile chorea
- Drugs
- APLA syndrome
- Neurodegenerative conditions: HD, neuroacanthocytosis, DRPLA
- Conception related: pregnancy, OCP's
- Endocrine: hyperthyroidism, hypo-, hyperglycemia


Coma causes checklist
AEIOU TIPS:
- Acidosis/ Alcohol
- Epilepsy
- Infection
- Overdosed
- Uremia
- Trauma to head
- Insulin: too little or or too much
- Pyschosis episode
- Stroke occurred
COMA: Coma and signicantly reduced conscious state causes
COMA
- CO2 and CO excess
- Overdose: TCAs, Benzos, EtOH, insulin, paracetamol, etc.
- Metabolic: BSL, Na+, K+, Mg2+, urea, ammonia, etc.
- Apoplexy: stroke, SAH, extradural, subdural, Ca, meningitis, encephalitis, cerebral abscess, etc.
Coma: conditions to exclude as cause
MIDAS:
- Meningitis
- Intoxication
- Diabetes
- Air (respiratory failure)
- Subdural/ Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Coma: differential
UNCONSCIOUS:
- Units of insulin
- Narcotics
- Convulsions
- Oxygen
- Nonorganic
- Stroke
- Cocktail
- ICP
- Organism
- Urea
- Shock
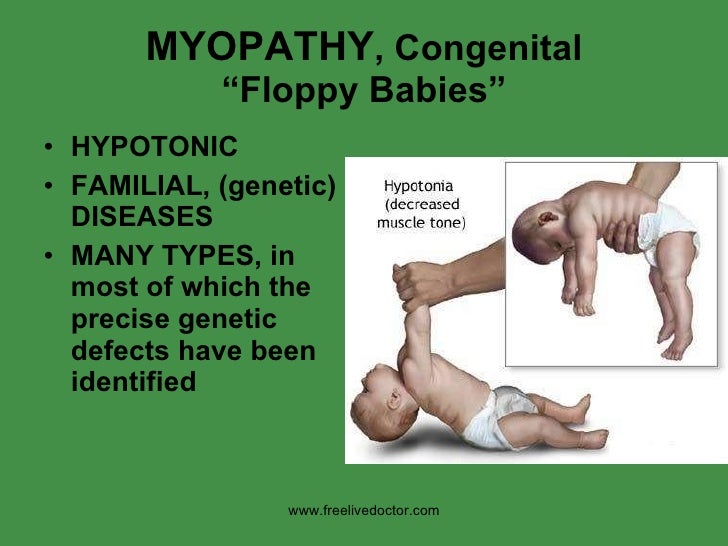
Congenital myopathy: features
DREAMS:
- Dominantly inherited, mostly
- Reflexes decreased
- Enzymes normal
- Apathetic floppy baby
- Milestones delayed
- Skeletal abnormalities
Coronal section of brain: structures
"In Extreme Conditions Eat People's Guts Instead of Their Hearts":
From insula to midline:
- Insula
- Extreme capsule
- Claustrum
- External capsule
- Putamen
- Globis pallidus
- Internal capsule
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus

Cranial nerves
"One Of Our Trained Teachers Asked For A Good, Vibrant And Hardworking Student ":
- Olfactory
- Optic
- Occulomotor
- Trochlear
- Trigeminal
- Abducens
- Facial
- Auditory
- Glossopharyngeal
- Vagus
- Accessory
- Hypoglossal

Cranial nerves: olfactory and optic numbers
"You have two eyes and one nose":
- Optic nerve is cranial nerve two.
- Olfactory nerve is cranial nerve one.
Alternatively, note alphabetical order: oLfactory, and oPtic.
Cranial nerves: sensory, motor or both
"Some Say Marry Money But My Brother Says Big Brains Matter More":
From I to XII:
- Sensory
- Sensory
- Motor
- Motor
- Both
- Motor
- Both
- Sensory
- Both
- Both
- Motor
- Motor
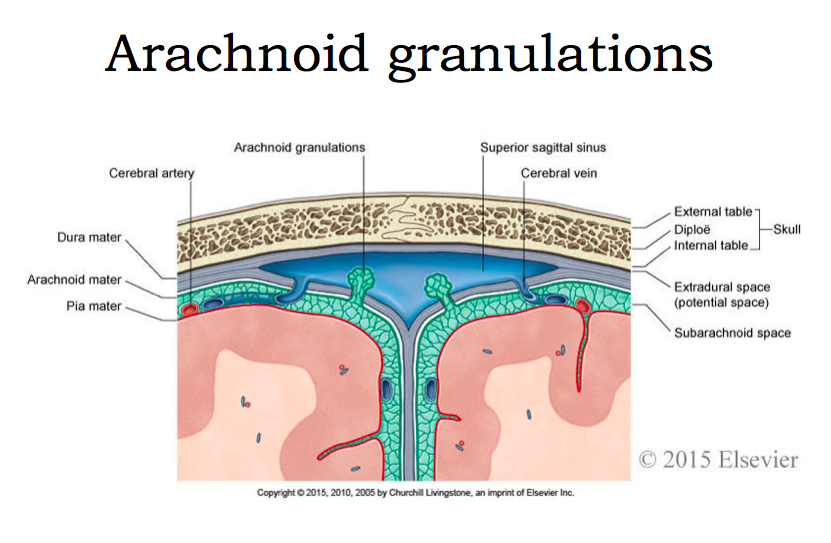
CSF circulation: function of choroid vs. arachnoid granules
- Choroid Creates CSF.
- Arachnoid granules Absorb CSF.
Dandy-Walker syndrome: components
"Dandy Walker Syndrome":
- Dilated 4th ventricle
- Water on the brain
- Small vermis
Dementia: reversible dementia causes
DEMENTIA:
- Drugs/ Depression
- Elderly
- Multi-infarct/ Medication
- Environmental
- Nutritional
- Toxins
- Ischemia
- Alcohol
Dementia: some common causes
DEMENTIA:
- Diabetes
- Ethanol
- Medication
- Environmental (eg CO poisoning)
- Nutritional
- Trauma
- Infection
- Alzheimer's

Dementia: treatable causes
DEMENTIA:
- Drug toxicity
- Emotional (depression, anxiety, OCD, etc.)
- Metabolic (electrolytes, liver dz, kidney dz, COPD)
- Eyes/ Ears (peripheral sensory restrictions)
- Nutrition (vitamin, iron deficiencies/ NPH [Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus]
- Tumors/ Trauma (including chronic subdural hematoma)
- Infection (meningitis, encephalitis, pneumonia, syphilis)
- Arteriosclerosis and other vascular disease

Dorsal= afferent, Ventral= efferent and their functions
"My friend DAVE got kicked in the behind and screamed":
- Dorsal/Afferent component is the sensation of pain coming from the rear.
- Ventral/Efferent component is the motor action of screaming (which is done at front of body).
Dysphagia vs. dysphasia
- DysphaSia is for Speech
- DysphaGia is for your Gut [swallowing].
Encephalitis: differential
HE'S LATIN AMERICAN:
- Herpesviridae
- Enteroviridae (esp. Polio)
- Slow viruses (esp. JC, prions)
- Syphilis
- Legionella/ Lyme disease/ Lymphocytic meningoencephalitis
- Aspergillus
- Toxoplasmosis
- Intracranial pressure
- Neisseria meningitidis
- Arboviridae
- Measles/ Mumps/ Mycobacterium tuberculosis/ Mucor
- E. coli
- Rabies/ Rubella
- Idiopathic
- Cryptococcus/ Candida
- Abscess
- Neoplasm/ Neurocysticercosis
*Neurocysticercosis should be assumed with recent Latin American immigrant patient unless proven otherwise.

Epilepsy: types, drugs of choice
"Military General Attacked Weary Fighters Pronouncing 'Veni Vedi Veci' After Crushing Enemies":
- Myoclonic
- Grand mal
- Atonic
- West syndrome
- Focal
- Petit mal (absence)
Respective drugsy:
- Valproate
- Valproate
- Valproate
- ACTH
- Carbamazepine
- Ethosuximide
Foramen ovale: contents
OVALE:
- Otic ganglion (just inferior)
- V3 cranial nerve
- Accessory meningeal artery
- Lesser petrosal nerve
- Emissary veins

GABA vs. Glu: the excitatory vs. inhibitory transmitter in brain (eg in basal ganglia)
- When you Glue two things together, you add (+) those things together, therefore Glu is the excitatory one (+).
- GABA is therefore the negative one.
Geniculate bodies: medial vs. lateral system
MALE:
Medial=Auditory. Lateral=Eye.
- Medial geniculate body is for auditory system, lateral geniculate body is for visual system.
- Can expand to MALES to remember Lateral=Eye=Superior colliculus (thus medial is inferior colliculus by default).
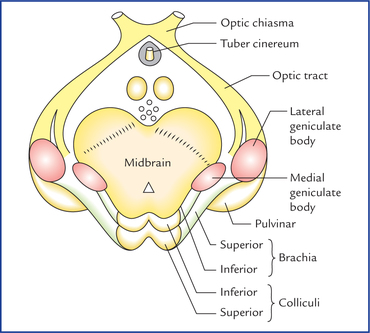
Geniculate bodies: paired to respective colliculi
SLIM:
- Superior colliculi: Lateral geniculate body.
- Inferior colliculi: Medial geniculate body.
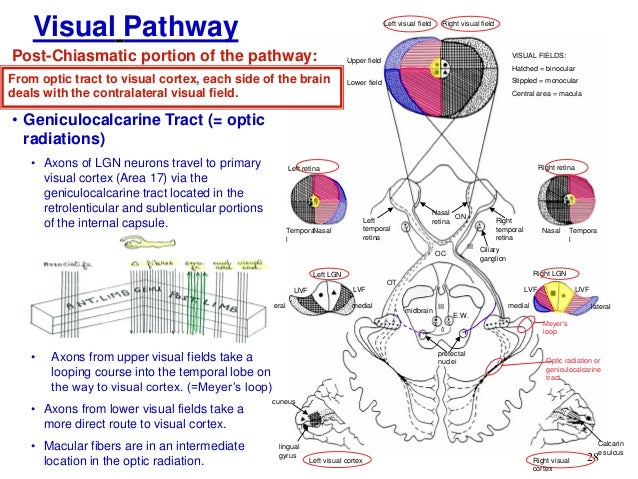
Geniculocalcarine tract:
Lower bank of calcarine sulcus is the Lingual gyrus: it receives input from Lower retinal quadrants.
Therefore, Cuneus is the Upper bank of calcarine sulcus: it receives input from Upper retinal quadrants.
Remember: lower retinal quadrants represent superior visual field quadrants and viceversa.
Head trauma: rapid neuro exam
12 P's:
- Psychological (mental) status
- Pupils: size, symmetry, reaction
- Paired ocular movememts
- Papilloedema
- Pressure (BP, increased ICP)
- Pulse and rate
- Paralysis, Paresis
- Pyramidal signs
- Pin prick sensory response
- Pee (incontinent)
- Patellar relex (and others)
- Ptosis
*Reevaluate patient every 8 hrs.
Huntington's: chromosome, involvement
HUNT 4 DATE:
- HUNTington's on chromosome 4, with cauDATE nucleus involvement.

Hypothalamus: feeding vs.satiety center
"Late night snack":
- LATEral is snacking [feeding] center. Therefore, ventromedial is satiety center.
Hypothalamus: general functions
"TALE of the hypothalamus":
- Temperature
- Appetite
- Libido
- Emotion
ICU: confusion causes
ICU CONFUSION:
- ICU psychosis
- Cardiac output low [hypotension, post cardiac arrest]
- Uncontrolled temperature [hypo/hyperthermia]
- Convulsion [post ictal]
- Oxygen [hypoxia, hypercarbia]
- Nociception [pain]
- Full bladder
- Uremia
- Sugar [hypo/hyperglycemia]
- Infection
- Opiates
- Natremia [hypo/hyper]
Lower vs. upper motor neuron lesion effects
1. "STORM, Baby"
2. 'In a Lower motor neuron lesion, everything goes Down:
STORM Baby tells you effects:
- Strength
- Tone
- Other
- Reflexes
- Muscle mass
- Babinski's sign
*In Lower all things go down: strength, tone, reflexes, muscle mass, and the big toe down in plantar reflex (Babinski's sign is big toe up: toe up = UMNL)
Alzheimer's disease (AD):
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 06, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 06, 2018
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 06, 2018
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
May 06, 2018
Rating:










No comments