Human Nervous system
Human Nervous system
Bright Zoom Doctor,
The nervous system has two major parts:
Within the central nervous system is a system of hollow cavities called ventricles. The network of linked cavities in the brain (cerebral ventricles) is continuous with the central canal of the spinal cord. The ventricles are filled with cerebrospinal fluid which is produced by specialized epithelium located within the ventricles called the choroid plexus. Cerebrospinal fluid surrounds, cushions, and protects the brain and spinal cord from trauma. It also assists in the circulation of nutrients to the brain.
Central Nervous System:
Brain :
The brain is the control center of the body. It consists of three main components: the forebrain, the brainstem, and the hindbrain. The forebrain is responsible for a variety of functions including receiving and processing sensory information, thinking, perceiving, producing and understanding language, and controlling motor function. The forebrain contains structures such as the thalamus and hypothalamus which are responsible for such functions as motor control, relaying sensory information, and controlling autonomic functions. It also contains the largest part of the brain, the cerebrum. Most of the actual information processing in the brain takes place in the cerebral cortex.
Themidbrainand the hindbrain together make up the brainstem. The midbrain is the portion of the brainstem that connects the hindbrain and the forebrain. This region of the brain is involved in auditory and visual responses as well as motor function.
The hindbrain extends from the spinal cord and contains structures such as the pons and cerebellum. These regions assist in maintaining balance and equilibrium, movement coordination, and the conduction of sensory information. The hindbrain also contains the medulla oblongata which is responsible for controlling such autonomic functions as breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
Central Nervous System:
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a cylindrical shaped bundle of nerve fibers that is connected to the brain. The spinal cord runs down the center of the protective spinal column extending from the neck to the lower back. Spinal cord nerves transmit information from body organs and external stimuli to the brain and send information from the brain to other areas of the body. The nerves of the spinal cord are grouped into bundles of nerve fibers that travel in two pathways. Ascending nerve tracts carry sensory information from the body to the brain. Descending nerve tracts send information pertaining to motor function from the brain to the rest of the body.
Central Nervous System:
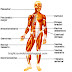
Neurons
Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system. All cells of the nervous system are comprised of neurons. Neurons contain nerve processes which are "finger-like" projections that extend from the nerve cell body. The nerve processes consist of axons and dendrites which are able to conduct and transmit signals. Axons typically carry signals away from the cell body. They are long nerve processes that may branch out to convey signals to various areas. Dendrites typically carry signals toward the cell body. They are usually more numerous, shorter and more branched than axons. Axons and dendrites are bundled together into what are called nerves. These nerves send signals between the brain, spinal cord, and other body organs via nerve impulses. Neurons are classified as either motor, sensory, or interneurons. Motor neurons carry information from the central nervous system to organs, glands, and muscles. Sensory neurons send information to the central nervous system from internal organs or from externa stimuli. Interneurons relay signals between motor and sensory neuron.
2. The peripheral nervous system (PNS).
- The peripheral nervous system consists of 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves. Some of those nerve pairs are exclusively sensory cells, such as those involved in smell and vision. Others are exclusively motor cells, such as those involved with eyeballs and hearing. Also, there are nerve pairs that have both sensory and motor cells, such as those involved in taste and some aspects of swallowing.
- Sensory cells carry messages to the central nervous system. Motor cells carry the signal from the central nervous system to the internal organs, muscles, and glands in the periphery or the outer edges of the body. Both types of cells travel together to the spinal cord, but then they separate into two areas. One area is called the posterior sensory root and the other is called the anterior sensory root.
- The motor nerve cells are either somatic or autonomic. The somatic nerve cells carry messages from the outer areas of the body having to do with the senses. It is like a passageway from the environment to the central nervous system. That seems simple compared to the autonomic cells because the autonomic nerve cells are divided into three separate divisions called the parasympathetic, the sympathetic, and the enteric divisions.
- These divisions are named by the functions that they are involved in throughout the body. This will be discussed later in detail in the lesson, but as a sneak preview, here is a brief description for each division. The parasympathetic division is involved with slowing body functions; while the sympathetic division increases body functions. The enteric division is involved with all the functions in the gastrointestinal areas, such as the pancreas and gallbladder.
Human Sensory system
1.Ey1.Eyes (Vision)
The eye is the organ of vision. It has a complex structure consisting of a transparent lens that focuses light on the retina. The retina is covered with two basic types of light-sensitive cells-rods and cones. The cone cells are sensitive to color and are located in the part of the retina called the fovea, where the light is focused by the lens. The rod cells are not sensitive to color, but have greater sensitivity to light than the cone cells. These cells are located around the fovea and are responsible for peripheral vision and night vision. The eye is connected to the brain through the optic nerve. The point of this connection is called the "blind spot" because it is insensitive to light. Experiments have shown that the back of the brain maps the visual input from the eyes.
The brain combines the input of our two eyes into a single three-dimensional image. In addition, even though the image on the retina is upside-down because of the focusing action of the lens, the brain compensates and provides the right-side-up perception. Experiments have been done with subjects fitted with prisms that invert the images. The subjects go through an initial period of great confusion, but subsequently they perceive the images as right side up.
The range of perception of the eye is phenomenal. In the dark, a substance produced by the rod cells increases the sensitivity of the eye so that it is possible to detect very dim light. In strong light, the iris contracts reducing the size of the aperture that admits light into the eye and a protective obscure substance reduces the exposure of the light-sensitive cells. The spectrum of light to which the eye is sensitive varies from the red to the violet. Lower electromagnetic frequencies in the infrared are sensed as heat, but cannot be seen. Higher frequencies in the ultraviolet and beyond cannot be seen either, but can be sensed as tingling of the skin or eyes depending on the frequency. The human eye is not sensitive to the polarization of light, i.e., light that oscillates on a specific plane. Bees, on the other hand, are sensitive to polarized light, and have a visual range that extends into the ultraviolet. Some kinds of snakes have special infrared sensors that enable them to hunt in absolute darkness using only the heat emitted by their prey. Birds have a higher density of light-sensing cells than humans do in their retinas, and therefore, higher visual acuity.
2.Ears (hearing)
The ear is the organ of hearing. The outer ear protrudes away from the head and is shaped like a cup to direct sounds toward the tympanic membrane, which transmits vibrations to the inner ear through a series of small bones in the middle ear called the malleus, incus and stapes. The inner ear, or cochlea, is a spiral-shaped chamber covered internally by nerve fibers that react to the vibrations and transmit impulses to the brain via the auditory nerve. The brain combines the input of our two ears to determine the direction and distance of sounds.
The inner ear has a vestibular system formed by three semicircular canals that are approximately at right angles to each other and which are responsible for the sense of balance and spatial orientation. The inner ear has chambers filled with a viscous fluid and small particles (otoliths) containing calcium carbonate. The movement of these particles over small hair cells in the inner ear sends signals to the brain that are interpreted as motion and acceleration.
The human ear can perceive frequencies from 16 cycles per second, which is a very deep bass, to 28,000 cycles per second, which is a very high pitch. Bats and dolphins can detect frequencies higher than 100,000 cycles per second. The human ear can detect pitch changes as small as 3 hundredths of one percent of the original frequency in some frequency ranges. Some people have "perfect pitch", which is the ability to map a tone precisely on the musical scale without reference to an external standard. It is estimated that less than one in ten thousand people have perfect pitch, but speakers of tonal languages like Vietnamese and Mandarin show remarkably precise absolute pitch in reading out lists of words because pitch is an essential feature in conveying the meaning of words in tone languages. The Eguchi Method teaches perfect pitch to children starting before they are 4 years old. After age 7, the ability to recognize notes does not improve much.
3.Tongue (taste)
The receptors for taste, called taste buds, are situated chiefly in the tongue, but they are also located in the roof of the mouth and near the pharynx. They are able to detect four basic tastes: salty, sweet, bitter, and sour. The tongue also can detect a sensation called "umami" from taste receptors sensitive to amino acids. Generally, the taste buds close to the tip of the tongue are sensitive to sweet tastes, whereas those in the back of the tongue are sensitive to bitter tastes. The taste buds on top and on the side of the tongue are sensitive to salty and sour tastes. At the base of each taste bud there is a nerve that sends the sensations to the brain. The sense of taste functions in coordination with the sense of smell. The number of taste buds varies substantially from individual to individual, but greater numbers increase sensitivity. Women, in general, have a greater number of taste buds than men. As in the case of color blindness, some people are insensitive to some tastes.
4.Nose (smell)
The nose is the organ responsible for the sense of smell. The cavity of the nose is lined with mucous membranes that have smell receptors connected to the olfactory nerve. The smells themselves consist of vapors of various substances. The smell receptors interact with the molecules of these vapors and transmit the sensations to the brain. The nose also has a structure called the vomeronasal organ whose function has not been determined, but which is suspected of being sensitive to pheromones that influence the reproductive cycle. The smell receptors are sensitive to seven types of sensations that can be characterized as camphor, musk, flower, mint, ether, acrid, or putrid. The sense of smell is sometimes temporarily lost when a person has a cold. Dogs have a sense of smell that is many times more sensitive than man's.
5.Skin (touch)
The sense of touch is distributed throughout the body. Nerve endings in the skin and other parts of the body transmit sensations to the brain. Some parts of the body have a larger number of nerve endings and, therefore, are more sensitive. Four kinds of touch sensations can be identified: cold, heat, contact, and pain. Hairs on the skin magnify the sensitivity and act as an early warning system for the body. The fingertips and the sexual organs have the greatest concentration of nerve endings. The sexual organs have "erogenous zones" that when stimulated start a series of endocrine reactions and motor responses resulting in orgasm.
Human Nervous system
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
 Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:
Reviewed by Bright Zoom
on
October 07, 2021
Rating:












No comments